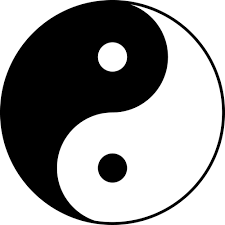
It is impossible to understand the basics of traditional Chinese medicine without understanding the concept of Yin and Yang. In order to do that we need to go back in time and visit the farmers and peasants of Ancient China. (1) Depending on nature for food and general survival the ancient Chinese farmers have been observing nature’s cycles for years to figure out some interconnection and interdependence within phenomena. They observed that phenomena is divided in oppositions, which tend to define and somehow account for one another. There was a day and a night, darkness and light, activity and rest. Without the day there was no night, there was no need of rest it there was no activity, etc. The peasants categorized these mutually self- defined oppositions in two divergent aspects. The day and everything that goes with it - the sun, the light, activity and warmth became Yang, while the night, the moon, the darkness, the stillness, and the cold became Yin. Since heaven is where the sun is, heaven is Yang, while it’s “opposite” – the earth is Yin. Heaven where the sun and the stars travel relates to time, thus time is Yang, while the earth can be measured and divided, and relates to space, thus space is Yin, etc… (1)
Next the ancient Chinese peasants observed that the oppositions Yin and Yang are not two separate existing units but two connected interdependent entities. There could be no day without a night and there could be no night without a day; the day transforms to become a night, while the night transforms to become a day; the day consumes the night and the night consumes the day; there is always a little day in the night and a little night in the day.
All these relationships of opposition, interdependence, mutual consumption and inter-transformation depict the simple yet fluid duality of our world.
YS
(1) Maciocia, Giovanni (1989). The Foundations of Chinese Medicine. Nanjing: Harcourt Publishers Limited
Related Articles:
Yin and Yang in Chinese Medicine
Five Elements in Chinese Medicine
The Spleen in Chinese Medicine
The Kidney in Chinese Medicine